Chapter4 (Part3)
4.8a(2) Isometric Projection of Pentagonal Prism:
For making isometric projection of pentagonal prism, enclose the base of prism i.e. pentagonal in a rectangle ABCD and locate the contact point of pentagon E, F, G, H & I on line AB, BC, CD & AD as shown in fig (4.21A). Now draw a box (dimensions a, b, & c as Length, width & Height respectively) in vertical position in isometric projection as shown in fig (4.21B). On the edges AB, BC, CD, AD, A’B’, B’C’, C’D’ & A’D’ of Box locate E, F, G, H, I, E’, F’, G’, H’ & I’. Now draw pentagons on the bottom & top faces of Box by making EF, FG, GH, HI, EI, E’F’, F’G’, G’H’, H’I’& E’I’. Now Join E to E’, F to F’, G to G’, H to H’ & I to I’ and complete the isometric projection of Pentagonal Prism.
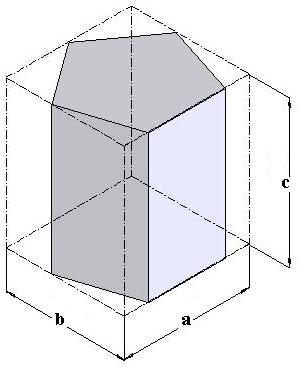
Fig (4.20): Pictorial drawing of Pentagonal prism within a Box
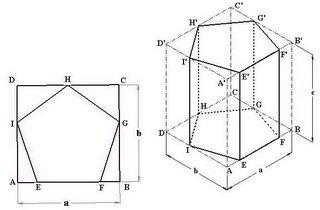
Fig (4.21): Method to draw isometric projection of Pentagonal prism. (A) Pentagon enclosed in Rectangle ABCD, (B) Pentagonal Prism enclosed by Box.
4.8a(3) Isometric Projection of Hexagonal Prism:
For making isometric projection of Hexagonal prism, enclose the base of prism i.e. Hexagon in a rectangle ABCD and locate the contact point of Hexagon E, F, G, H, I & J on line AB, BC, CD & AD as shown in fig (4.23A). Now draw a box (dimensions a, b, & c as Length, width & Height respectively) in vertical position in isometric projection as shown in fig (4.23B). On the edges AB, BC, CD, AD, A’B’, B’C’, C’D’ & A’D’ of Box locate E, F, G, H, I, J, E’, F’, G’, H’ I’ & J’. Now draw Hexagons on the bottom & top faces of Box by making EF, FG, GH, HI, EI, IJ, E’F’, F’G’, G’H’, H’I’, E’I’ & I’J’. Now Join E to E’, F to F’, G to G’, H to H’, I to I’ & J to J’ and complete the isometric projection of Hexagonal Prism.

Fig (4.22): Pictorial drawing of Hexagonal prism within a Box
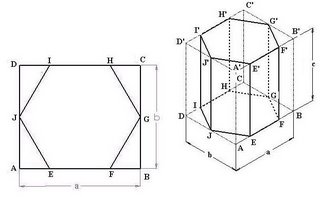
Fig (4.23): Method to draw isometric projection of Hexagonal prism. (A) Hexagon enclosed in Rectangle ABCD, (B) Hexagonal Prism enclosed by Box
In the same way isometric projection of the Hexagonal prism can be drawn in other isometric axes as shown in fig (4.25).

Fig (4.24): Pictorial drawing of Hexagonal prism within a Box when the prism axis is parallel to other isometric axis
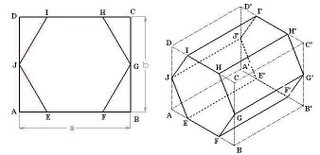
Fig (4.25): Method to draw isometric projection of Hexagonal prism in other isometric axis. (A) Hexagon enclosed in Rectangle ABCD, (B) Hexagonal Prism enclosed by Box.
4.8b. Pyramids:
A pyramid has a triangle, square, rectangle or a polygon as its base & isosceles triangular faces equal to the number of edges of base polygon meeting at one point called apex.
When the axis of the pyramid is perpendicular to its base then it is known as right pyramid. Pyramids are also known by its base. Like triangular pyramid, square pyramid, pentagonal pyramid and so on.
To draw the isometric projection of pyramids, offset method can be used as an aid in addition to the boxing method.
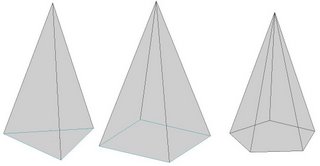
Fig (4.26): Different types of Pyramids. A) Triangular Pyramid B) Rectangular Pyramid C) Pentagonal Pyramid
4.8b(1) Isometric Projection of Triangular Pyramid:
Enclose the top view of triangular pyramid in a rectangle ABCD and draw parallel lines to AB & CD intersecting at point O, which is the centre of triangle ABG. In orthographic view (top view) measure the distance of point O from AB & BC i.e. e & d. Draw the rectangle ABCD on isometric axes. By locating the triangle points on Top view, draw the triangle in rectangle ABCD. Locate point O in rectangle ABCD on isometric projection. From this point O measure the height c and draw point O’ which is the apex of pyramid. From the apex point O’, join A, B & G and complete the Triangular pyramid. The above method can be adopted to draw the isometric projection of triangular pyramid in other axes.

Fig (4.27): Orthographic views (Top & Front view) and Isometric projection of Triangular Pyramid
4.8b(2) Isometric Projection of Square Pyramid:
In the top view of square pyramid locate the co-ordinates of point O, which is the centre of Square ABCD. Draw the square ABCD on isometric axes. Draw point O in square ABCD on isometric projection by seeing the co-ordinates from top view. From this point O measure the height c and draw point O’ which is the apex of pyramid. From the apex point O’, join A, B, C & D and complete the Square pyramid.
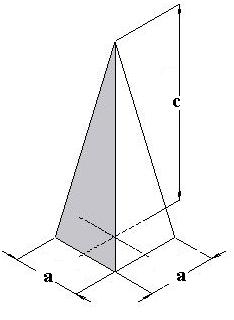
Fig (4.28): Pictorial drawing of Square pyramid with dimensions

Fig (4.29): Orthographic views (Top & Front view) and Isometric projection of Square Pyramid.
4.8b(3) Isometric Projection of Pentagonal Pyramid:
Enclose the top view of pentagonal pyramid in a rectangle ABCD and draw parallel lines to AB & CD intersecting at point O, which is the centre of pentagon EFHIJ. In orthographic view (top view) measure the distance of point O from AB & BC i.e. e & d. Draw the rectangle ABCD on isometric axes. By locating the pentagon points on Top view, draw the pentagon in rectangle ABCD. Locate point O in rectangle ABCD on isometric projection. From this point O measure the height c and draw point O’ which is the apex of pentagonal pyramid. From the apex point O’, join E, F, H, I & J and complete the Pentagonal pyramid.
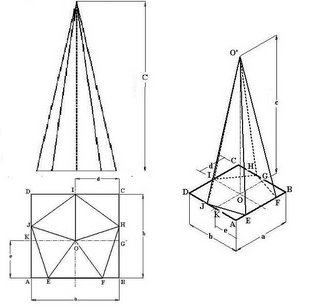
Fig (4.30): Orthographic views (Top & Front view) and Isometric projection of Pentagonal Pyramid.
4.8b(4) Isometric Projection of Hexagonal Pyramid:
Enclose the top view of Hexagonal pyramid in a rectangle ABCD and draw parallel lines to AB & CD intersecting at point O, which is the centre of Hexagon EFGHIJ. Draw the rectangle ABCD on isometric axes. By locating the Hexagon points on Top view, draw the Hexagon in rectangle ABCD. Locate point O in rectangle ABCD on isometric projection. From this point O measure the height c and draw point O’, which is the apex of Hexagonal pyramid. From the apex point O’, join E, F, G, H, I & J and complete the Hexagonal pyramid.
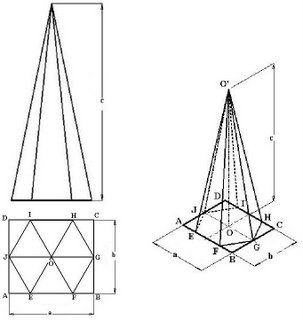
Fig (4.31): Orthographic views (Top & Front view) and Isometric projection of Hexagonal Pyramid.

